Drug Repurposing: Unlocking New Therapeutic Potentials
By PETC | June 5, 2025
Drug repurposing, also known as drug repositioning, involves identifying new therapeutic uses for existing medications. This approach offers a cost-effective and time-saving alternative to traditional drug development, leveraging known safety profiles to expedite the availability of treatments for various diseases.
Advantages of Repurposing
- Reduced Development Time: Utilizing existing drugs can significantly shorten the time required to bring a treatment to market.
- Cost Efficiency: Repurposing can reduce development costs by up to 85% compared to traditional methods. :contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}
- Improved Success Rates: Known safety profiles increase the likelihood of regulatory approval.
- Addressing Unmet Needs: Offers new treatment options for rare or neglected diseases. :contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2}
Notable Examples of Drug Repurposing
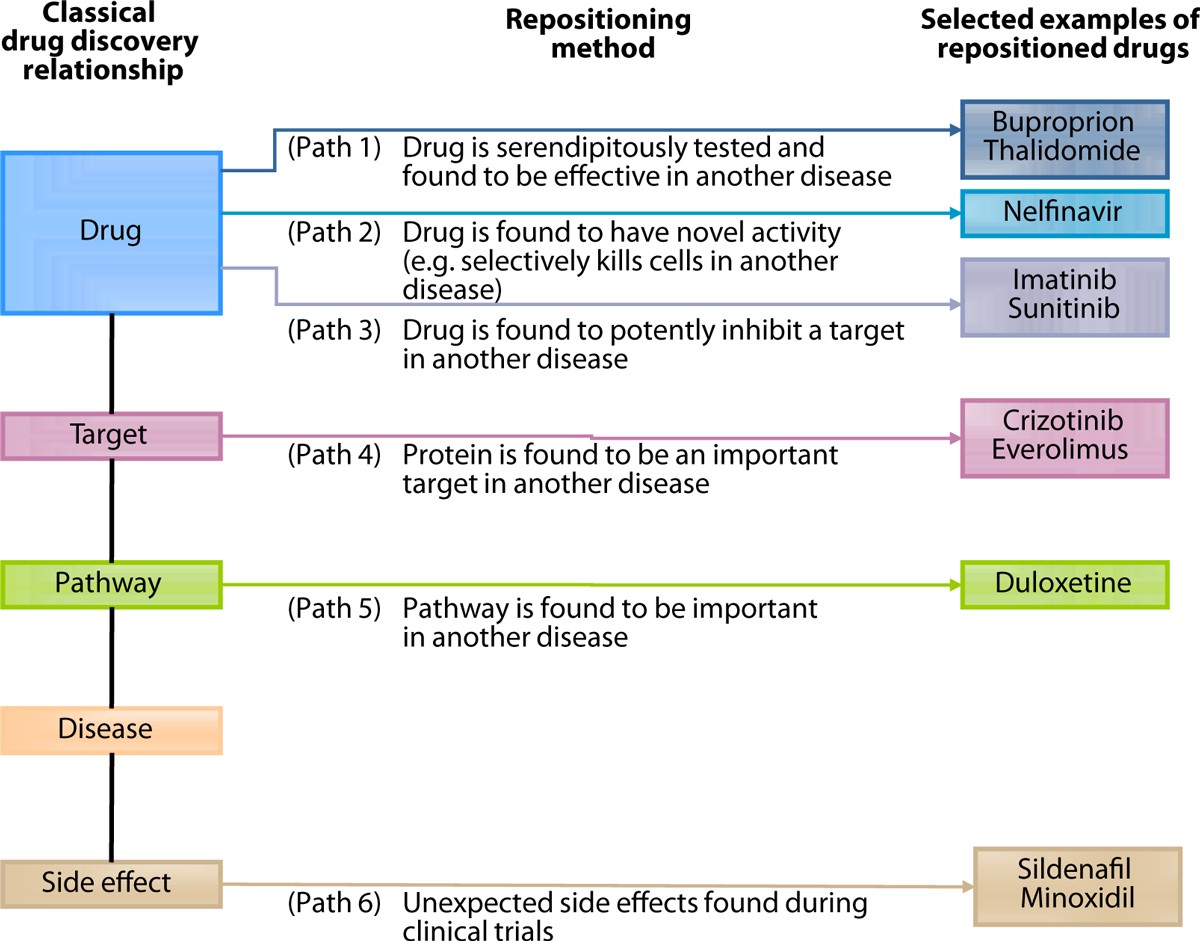
- Minoxidil: Initially developed for hypertension, later found effective for treating hair loss. :contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3}
- Thalidomide: Originally used as a sedative, now repurposed for multiple myeloma treatment. :contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}
- Everolimus: Initially an immunosuppressant, repurposed for treating tuberous sclerosis. :contentReference[oaicite:5]{index=5}
Challenges in Repurposing
- Intellectual Property Issues: Navigating patent laws can be complex when repurposing existing drugs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining approval for new indications requires thorough clinical validation.
- Limited Financial Incentives: Especially for generic drugs, profitability can be a concern. :contentReference[oaicite:6]{index=6}
Enhance your expertise in pharmaceutical sciences and prepare for the OPRA exam with our comprehensive course.
Conclusion
Drug repurposing presents a promising avenue for accelerating the development of effective treatments, especially in areas with unmet medical needs. By leveraging existing medications, we can reduce costs, shorten development timelines, and improve patient outcomes.